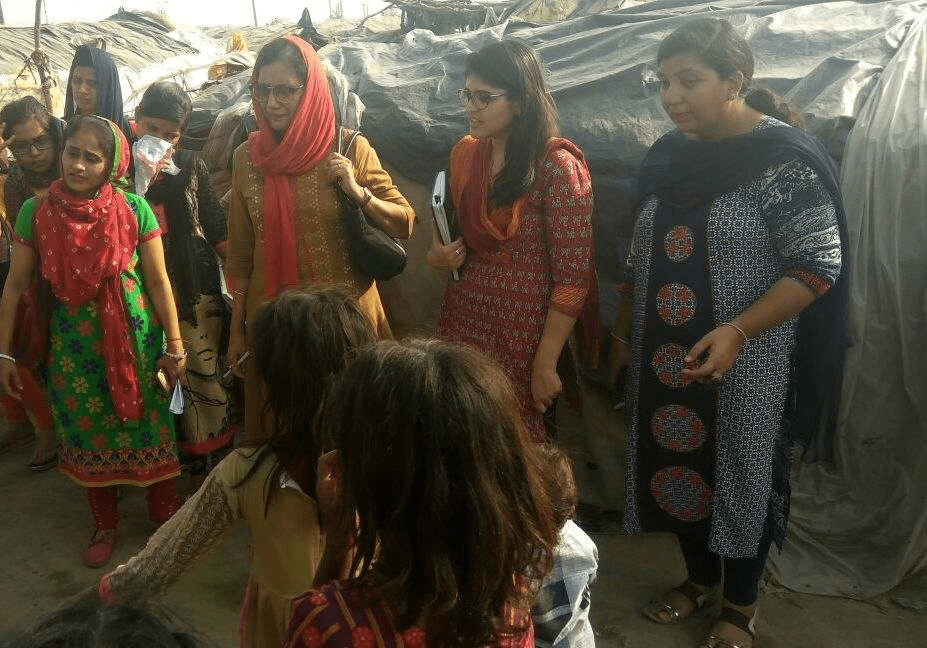In the vast and often intricate world of governance, achieving effective policy implementation is one of the toughest challenges faced by governments. Bridging the gap between well-intentioned policies and on-the-ground impact requires innovative approaches. Haryana is home to 3 crore+ citizens across its 22 districts, and driving change at this scale requires a set of thoughtful enablers, the ‘plumbing’, through which complex initiatives can flow. The Chief Minister’s Good Governance Associates (CMGGA) program, launched in 2016, is an exemplary model of how a collaborative partnership between young professionals and the government can lead to transformative changes in public administration.
The CMGGA program has proven to be a game-changer for the state of Haryana, making strides in areas such as education, healthcare, public service delivery, and water rejuvenation. Its success offers valuable lessons on how states across India can improve their governance through data-driven, participatory, and outcome-oriented initiatives.
Genesis of CMGGA: A Bold Vision for Governance Reform
The roots of the CMGGA program can be traced back to November 2015, when a simple but revolutionary idea was proposed: what if young, passionate, and skilled professionals could work directly with government officials to implement flagship initiatives. This vision became a reality in January 2016, with the signing of an MoU between the Government of Haryana and Ashoka University. This partnership laid the foundation for a program that grew to become India’s longest-running state-wide governance fellowship.
The program started as an experiment but soon evolved into a vital component of Haryana's administrative machinery. It was designed to act as a catalyst for the Chief Minister’s flagship initiatives, bringing in merit-based recruitment to ensure that the best talent was involved in making a real impact on the ground. With a focus on governance transformation and quality implementation, the CMGGA program has empowered the 22 districts across Haryana to function more effectively.
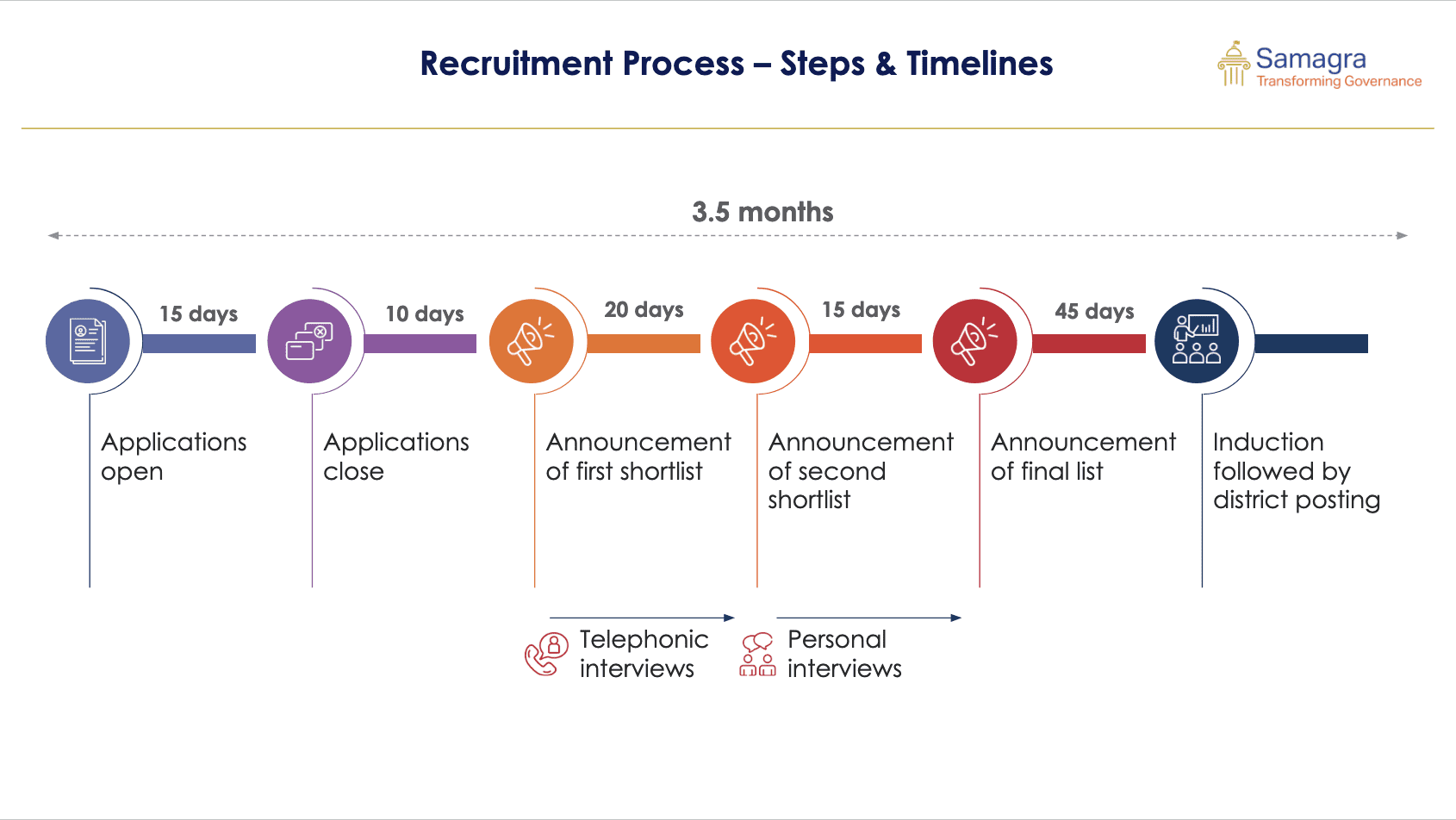
With a 3.5 month long rigorous recruitment process, the program ensures that a set of diverse, capable young professionals are selected each year. The entire process was conducted at an arm’s length from the government to ensure meritocracy. These associates, who must be under 28 years of age and have at least one year of work experience or a postgraduate degree, are embedded within district administrations. Here, they work directly with the District Commissioners (DCs) and other government officials, contributing to the implementation of key initiatives and finding innovative solutions to local governance problems. Over the years, seven cohorts of CMGGAs have driven significant changes in Haryana’s governance landscape.
The Two Pillars: A Unique Approach to Governance
The CMGGA program operates on two fundamental pillars—Associate Management and the Impact Cycle. These two frameworks ensure that associates are well-prepared for the challenges of governance while following a structured approach that leads to tangible, measurable outcomes.
1. Associate Management
The process of Associate Management begins with the merit-based selection of young professionals, ensuring that those chosen are skilled, passionate, and aligned with the program’s goals. However, the management of Associates extends far beyond recruitment. It focuses on providing them with the tools, training, and support needed to make a difference in their respective districts.
Associates begin their fellowship with an intensive bootcamp-style induction program. This not only sets expectations but also equips them with essential skills in governance functioning, stakeholder management, project implementation, and data analysis. By blending theoretical knowledge with practical fieldwork, the program creates an environment of experiential learning where Associates are constantly learning and adapting.
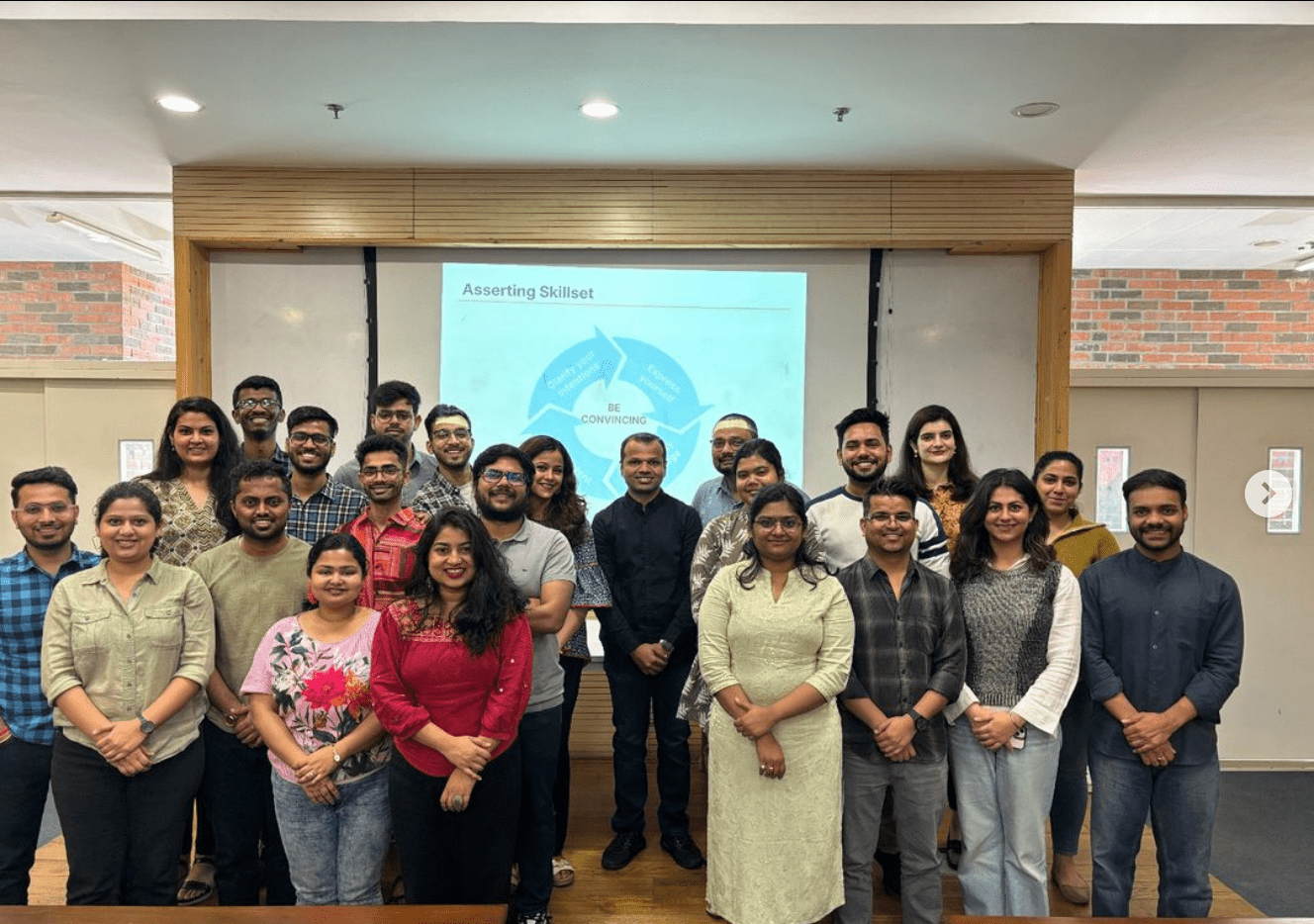
CMGGA team in a skill-building forum at Ashoka University
The Field + Forum approach is another unique feature of the CMGGA program. Associates spend seven weeks in the field, immersed in district-level governance, followed by one week in a structured forum where they reflect on their work, engage in skill-building sessions, and receive feedback from experts and mentors. This process not only helps Associates refine their strategies but also ensures that they are aligned with the broader goals of the program.
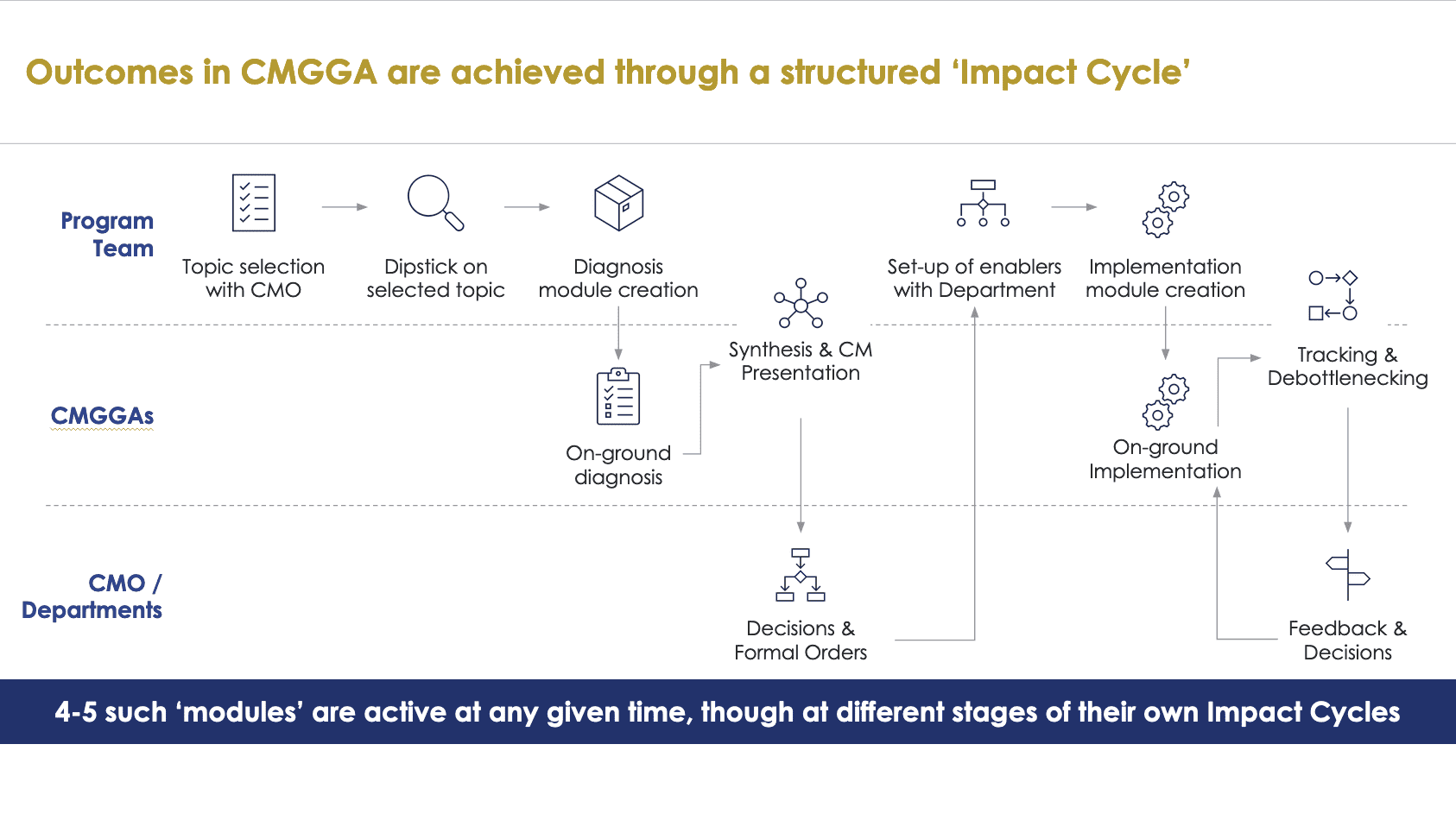
2. The Impact Cycle
The Impact Cycle is the backbone of the CMGGA program’s operational model. Every project or initiative follows a structured cycle that ensures systematic diagnosis, implementation, and monitoring. This cycle involves:
- Topic Selection: Associates work closely with the Chief Minister’s Office (CMO) to identify priority areas that need intervention. This ensures that the efforts of the Associates are aligned with the larger policy objectives of the state.
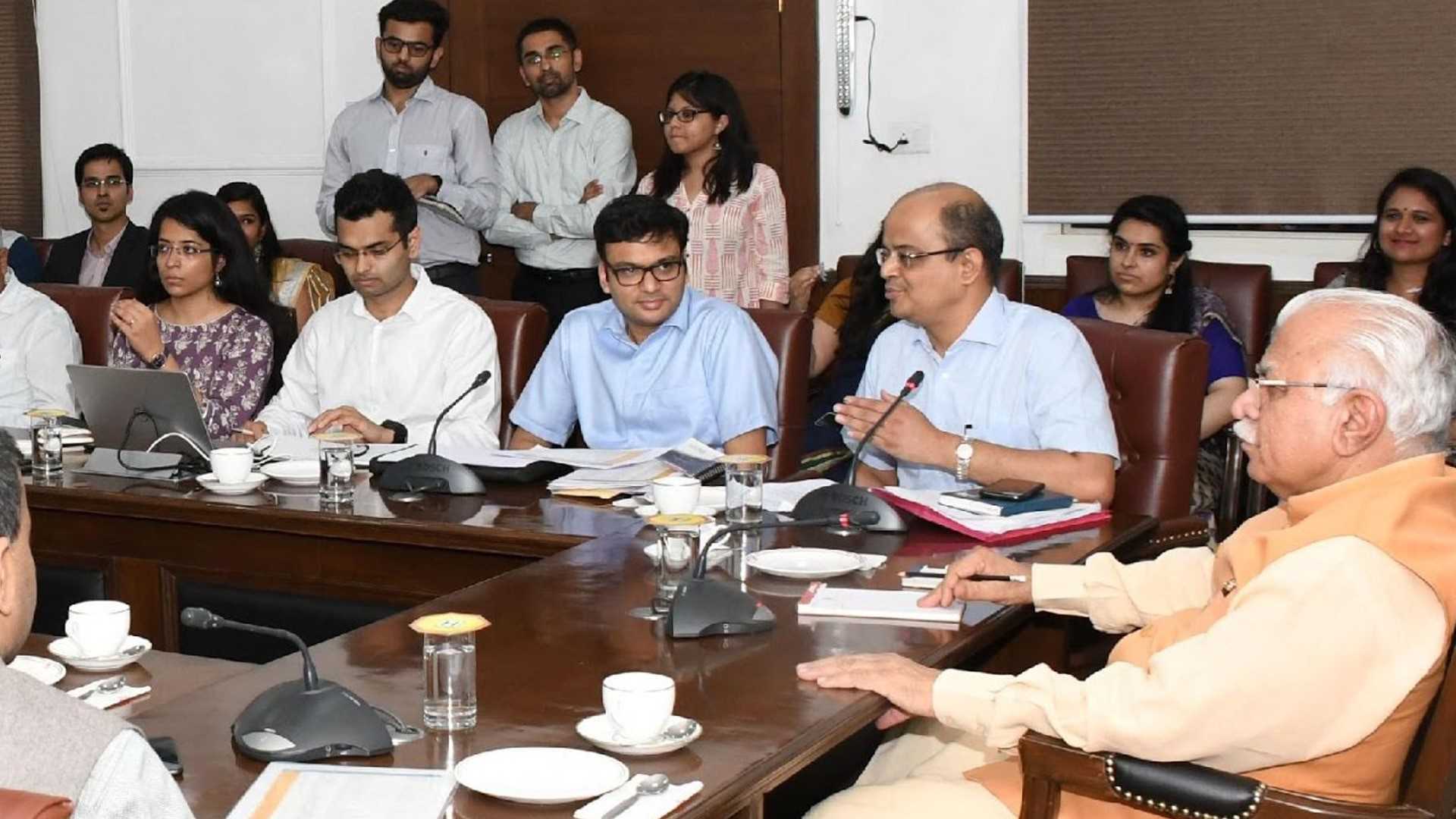
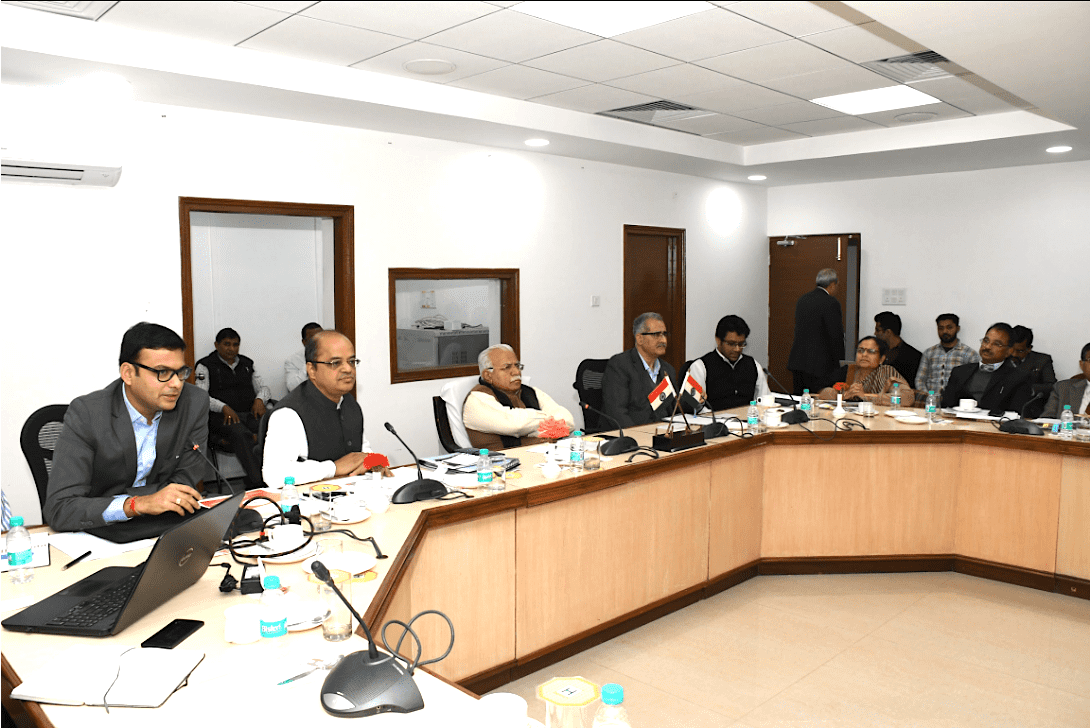
CMO Meeting on priorities of the state
- Diagnosis Module: The Associates then engage in a comprehensive diagnosis of the issue, using data collection, surveys, and on-ground research. This step helps in identifying bottlenecks and challenges faced during the implementation of policies at the grassroots level.
- Implementation Module: Based on the diagnosis, an actionable implementation plan is designed, which the Associates then execute. This step involves working with district administration, local governments, and other key stakeholders.
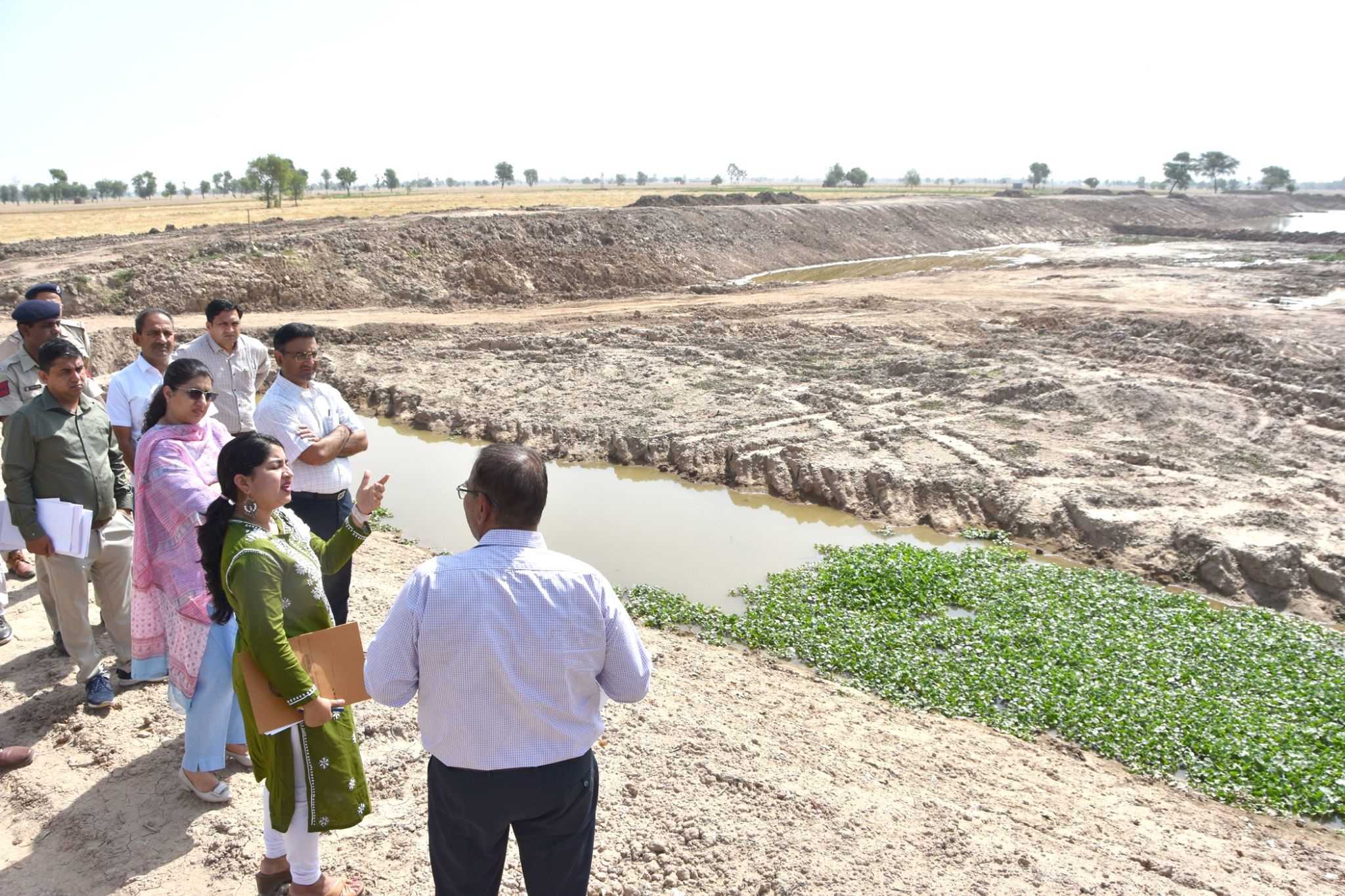
CMGGA evaluating on ground implementation in Karnal
- Tracking and Debottlenecking: As the implementation progresses, the Associates monitor the progress and address any bottlenecks that arise. This ensures that issues are addressed in real-time, preventing delays and ensuring the smooth rollout of programs.
Tracking sheet for managing progress of district level outcomes
- Feedback and Reporting: After implementation, the results are synthesized into a report that is shared with the CMO and other government bodies. This feedback loop allows for continuous improvement and adaptation of strategies.
CMO meeting on achievements and outcomes
The cyclical nature of this process ensures that the program is both dynamic and responsive to the needs of the districts. Moreover, by focusing on data-driven decision-making, the program ensures that government actions are based on evidence and field-level insights.
Key Flagship Initiatives and Their Impact
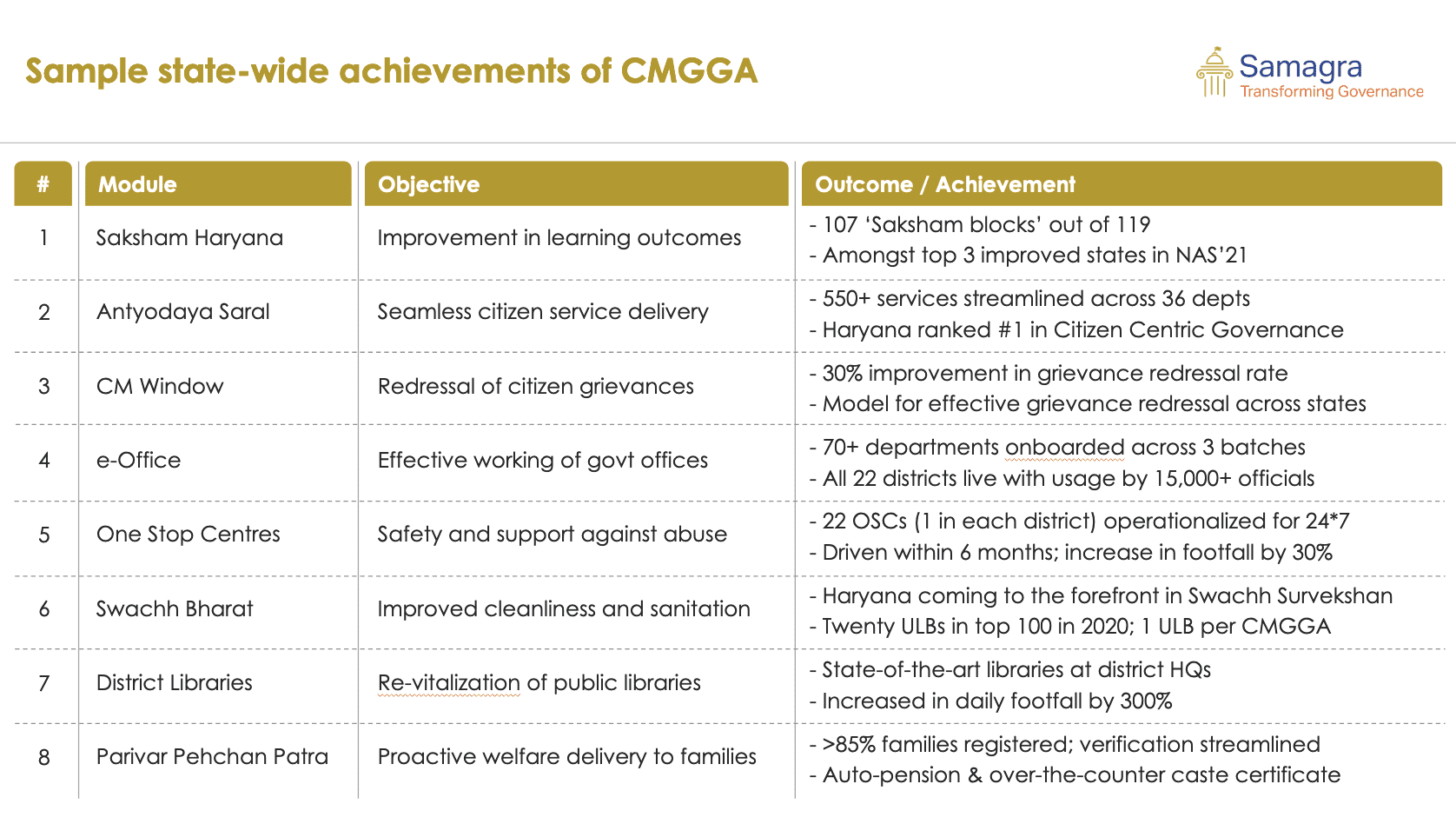
Since its inception, the CMGGA program has played a pivotal role in driving the success of several flagship initiatives in Haryana. By embedding young professionals within district administration and working closely with various government departments, the program has helped Haryana achieve significant milestones in governance.
1. Antyodaya Saral
The Antyodaya Saral initiative is one of the most impactful programs that CMGGAs have worked on. This initiative integrates over 550 schemes across 30 departments into a single, easy-to-access digital platform. This has drastically improved the ease of accessing government services for the people of Haryana. The program’s emphasis on transparency and efficiency won the National e-Governance Award in 2020, and Haryana achieved Rank 1 in NITI Aayog’s 2021 Index for ease of living.
2. Saksham Haryana
Education has been a cornerstone of the CMGGA program’s work. Under the Saksham Haryana initiative, the state has achieved remarkable success in improving education outcomes. The program’s focus on ensuring grade-level competency has impacted over 14,000 schools, benefitting 24 lakh students. The 14-rank jump in Haryana’s National Achievement Survey (NAS) score from 2017 to 2021 is a testament to the effectiveness of the initiative, which focuses on teacher training, curriculum development, and student assessments.
3. Amrit Sarovar
Water management and conservation are critical areas where the CMGGA program has driven meaningful change. The Amrit Sarovar initiative, aimed at rejuvenating Haryana’s water bodies, has successfully revived over 2,100 ponds, increasing water retention capacity by approximately 1,700 liters. This not only addresses the state’s water scarcity issues but also boosts local economies, with panchayat income increasing by over ₹14 crore through water management initiatives.
4. CM Window
The CM Window initiative is a flagship grievance redressal system that allows citizens to lodge complaints and receive prompt responses from the government. The program’s focus on enhancing the effectiveness of this system has led to a 30% improvement in the rate of grievance redressal. This initiative showcases the CMGGA program’s commitment to citizen-centric governance and its ability to foster trust between the government and the public.
5. Meri Fasal Mera Byora
Agriculture is the backbone of Haryana’s economy, and the Meri Fasal Mera Byora initiative has played a crucial role in improving the lives of farmers. This scheme, designed to streamline farmer registration and ensure timely access to government schemes, has benefitted over 500 farmers across 38 villages. By simplifying access to welfare programs, CMGGAs have helped bridge the gap between policies and on-the-ground impact.
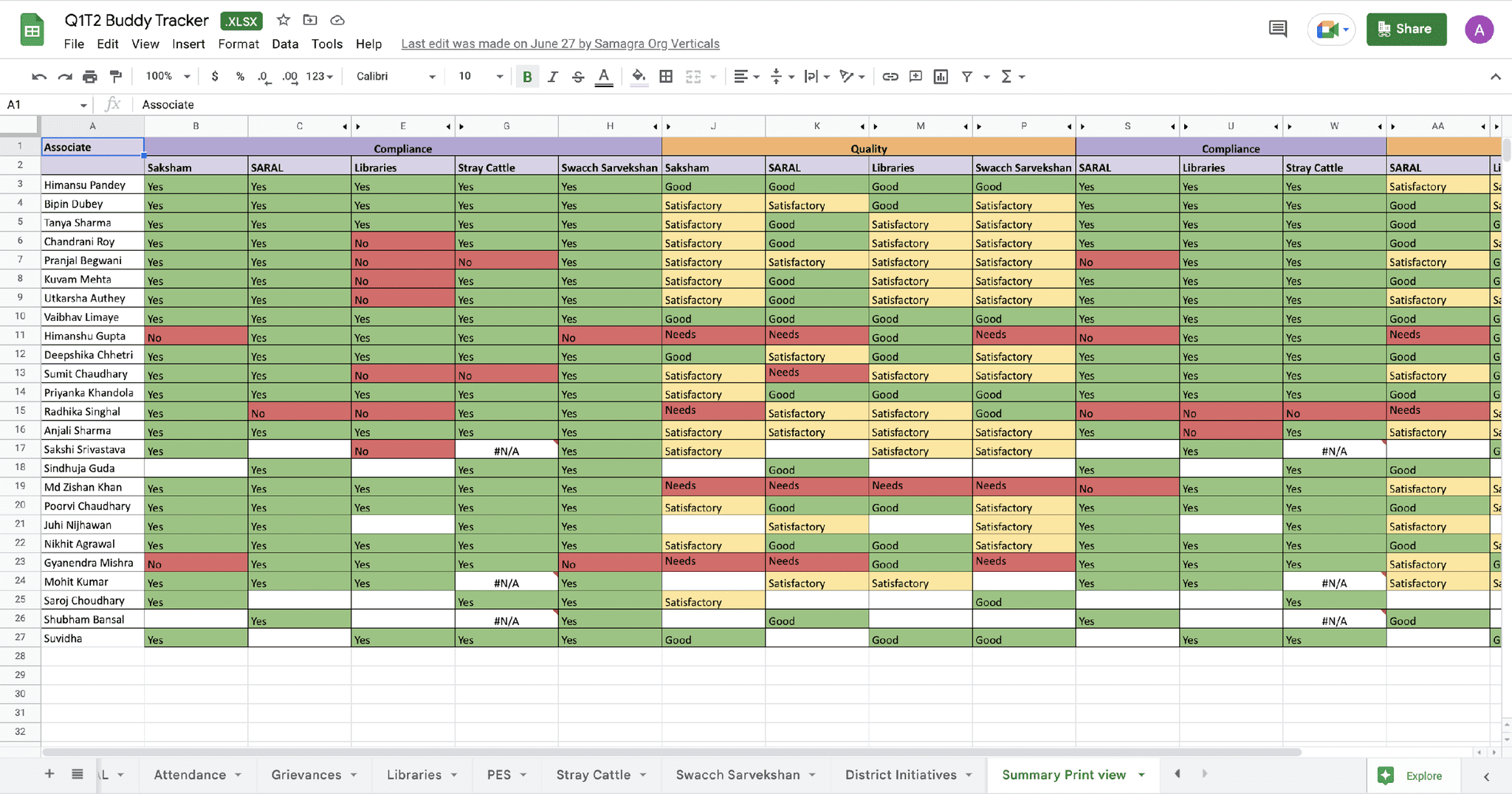
Some other statewide achievements of CMGGA are:
Expanding the Reach: Innovations at the District Level
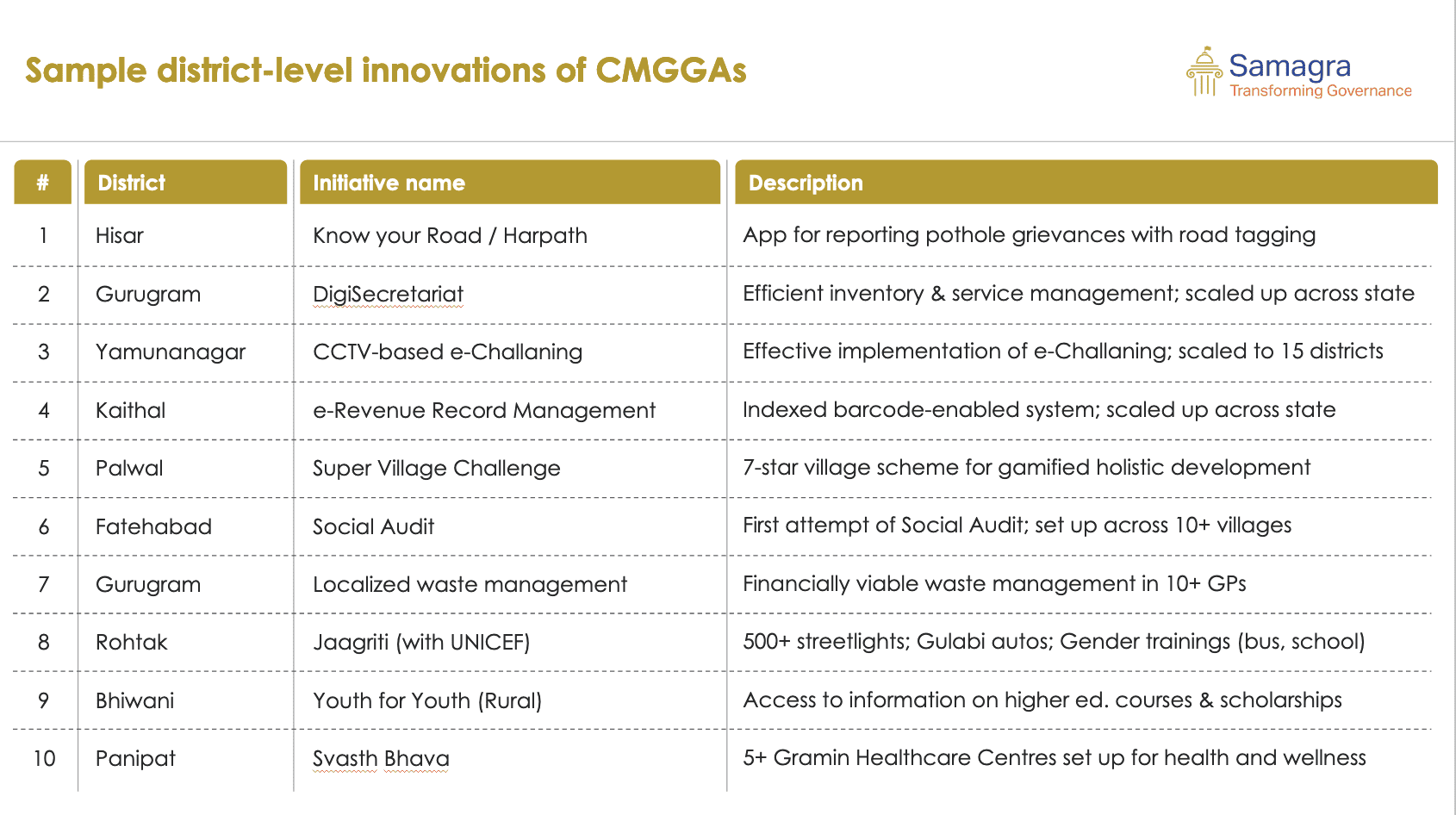
In addition to the flagship initiatives, CMGGAs have spearheaded several district-specific innovations that have potential for state-wide scale-up. Some of these projects are:
- Super Village Challenge: Launched in 2016-17, this challenge incentivizes village leaders to improve their communities by rewarding Sarpanches who achieve the best results across a range of development indicators. This initiative has led to the creation of 100+ new self-help groups, improvements in school infrastructure, and the declaration of 260 villages as polythene-free zones.
- Jagriti: This initiative, focused on safe mobility and gender inclusiveness, was a collaboration between CMO Haryana and UNICEF. By making public toilets accessible, introducing Gulabi Autos (women-run autos), and conducting gender training in schools, Jagriti has empowered women and improved safety in public spaces.
- Project ‘MILAP’ in Palwal: Aimed at improving institutional access for the public, MILAP created channels for citizens to engage more effectively with local government services, ensuring smoother service delivery.
These district-level initiatives demonstrate the program’s capacity for innovation and its ability to tailor solutions to local challenges while still aligning with state-wide goals.
Some other district level achievements of CMGGA are:
The Ripple Effect: Impact on Associates and the Administrative Culture
While the policy outcomes of the CMGGA program have been widely recognized, the program’s impact extends far beyond the immediate results. It has also played a significant role in shaping the administrative culture in Haryana and creating a pipeline of governance professionals who are now contributing to social impact sectors across India.
1. Impact on Associates
For the Associates themselves, CMGGA offers an unparalleled opportunity to work within the government and understand the inner workings of governance. Many Associates enter the program with an interest in policy and governance but leave with in-depth knowledge, practical skills, and a new perspective on how change can be driven at the grassroots level.
Over 70% of CMGGA alumni continue to work in the impact ecosystem, contributing to the social sector, public policy, and education reform. By equipping Associates with both theoretical knowledge and practical experience, the program has created a cadre of young leaders who are shaping the future of governance in India.
2. Impact on Administrative Culture
The CMGGA program has also brought about a cultural shift within Haryana’s bureaucracy. By introducing young, energetic professionals into the system, it has fostered a greater reliance on data, technology, and innovation. Moreover, the feedback loop created between the CMO, Associates, and district administrations ensures that policy decisions are informed by on-the-ground realities. This shift toward a data-driven approach and a focus on outcome-oriented governance has led to improvements in service delivery across the state.
Challenges Faced and Lessons Learned
While the CMGGA program has been largely successful, it has not been without challenges. The sheer size and complexity of Haryana’s bureaucratic machinery means that Associates often face resistance from local officials who are accustomed to traditional ways of working. However, by building strong relationships with DCs and government departments, and by relying on evidence-based decision-making, Associates have been able to overcome these obstacles.
Additionally, ensuring the sustainability of projects after the departure of Associates remains a key challenge. However, by involving local stakeholders from the beginning and creating long-term implementation plans, the program has taken steps to ensure that the benefits of its initiatives are sustained over time.
Conclusion: A Model for Future Governance
The Chief Minister’s Good Governance Associates (CMGGA) program stands as a testament to the power of collaboration between young professionals and government systems. Through its structured Impact Cycle, the program has driven measurable changes in Haryana’s governance while fostering a new generation of governance professionals who are committed to making a difference.
As the program comes to a pause after its eighth year, it leaves behind a rich legacy of innovation, efficiency, and citizen-centric governance. Haryana’s experience with CMGGA offers valuable lessons for other states and countries looking to improve their governance frameworks. By investing in young talent, fostering data-driven decision-making, and maintaining a continuous feedback loop between government officials and the people they serve, the CMGGA program has set a new benchmark for governance in India.
The program’s success and its ripple effects on governance, policy, and youth engagement highlight the potential for similar models to be replicated across the country, paving the way for a new era of governance that is more inclusive, responsive, and effective.